Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Table of contents
- What is Radar Image Brightness?
- How Does Surface Roughness Affect Radar Image Brightness?
- What Role Does Viewing Angle Play in Radar Image Brightness?
- How Does Moisture Content Influence Radar Image Brightness?
- Why is Look Direction Important in Radar Images?
- What Are Corner Reflectors and How Do They Affect Radar Image Brightness?
- Why is Understanding Radar Image Brightness Important?
- You Might Also Like
Radar images are widely used in remote sensing to study the Earth’s surface. But have you ever wondered why some objects look bright while others look dark in these images? The answer lies in Radar Image Brightness, which depends on how much energy is reflected back to the radar sensor after hitting the surface.
This reflection is influenced by factors like surface roughness, viewing angle, moisture content, and structural geometry. Understanding these factors makes it easier to correctly interpret radar images for applications in agriculture, urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.
What is Radar Image Brightness?
Radar Image Brightness refers to how bright or dark an object appears in a radar image. Bright areas indicate strong reflections of radar waves, while dark areas indicate weaker reflections. This brightness is not about visible light but about the microwave energy returned to the radar sensor.
How Does Surface Roughness Affect Radar Image Brightness?
One of the main factors affecting radar brightness is surface roughness. Imagine shining a flashlight on two surfaces—one a smooth glass table and the other a rough concrete wall. The glass reflects light in one direction, making it difficult to see unless you’re looking from the right angle. The concrete, on the other hand, scatters light in multiple directions, making it more visible from different viewpoints. Similarly, in radar imaging:
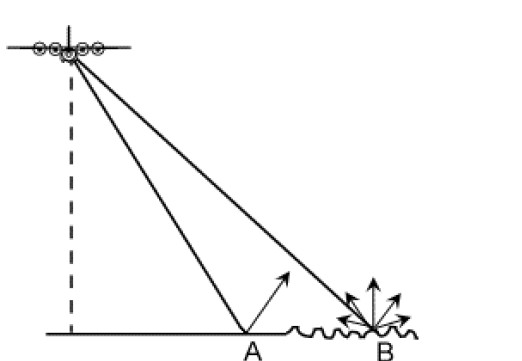
A smooth surface A (such as calm water or a paved road) reflects radar waves away from the sensor, making it appear dark in the image.
A rough surface B (such as rocky terrain or a dense forest) scatters the radar waves in different directions, sending more energy back to the radar, making it appear bright.
👉 Example: A dry road will look darker in a radar image, while a grass field appears brighter due to rougher texture.
What Role Does Viewing Angle Play in Radar Image Brightness?
The angle at which the radar beam hits a surface also plays a crucial role in determining brightness. Think about how the sun casts shadows throughout the day. In the morning and evening, shadows are long because the sun is at a low angle, but at noon, shadows are short because the sun is directly overhead. Similarly, in radar imaging:
The angle at which the radar beam hits the surface changes how much energy is reflected:
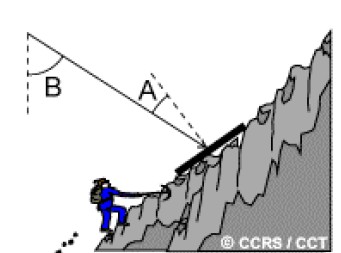
When a slope faces the radar, it reflects more energy back to the sensor, appearing brighter in the image.
When a slope faces away from the radar, less energy is reflected back, making it darker or even shadowed.
👉 Example: In radar images of mountains, one side may appear very bright while the opposite side looks almost black.
How Does Moisture Content Influence Radar Image Brightness?
Moisture greatly impacts brightness:
- Wet surfaces reflect more energy → appear brighter.
- Dry surfaces absorb more energy → appear darker.
👉 Example: After rainfall, agricultural fields and forests look brighter in radar images compared to dry conditions. This is why radar is used for soil moisture monitoring, flood detection, and drought assessment.
Why is Look Direction Important in Radar Images?
Think about a row of books on a shelf. If you shine a light directly at the spines, they all appear clearly. But if you shine the light from the side, some books will cast shadows, making it harder to see details. Similarly, the look direction of a radar sensor affects how we see objects in an image.
- If the radar beam is perpendicular to a surface feature, more energy is reflected back, making the feature appear brighter.
- If the radar beam is angled, less energy returns to the radar, making the feature darker.
This effect is particularly noticeable in cities where tall buildings and roads create complex patterns of brightness and shadows. By changing the radar’s look direction, we can enhance certain features while minimizing distortions.
What Are Corner Reflectors and How Do They Affect Radar Image Brightness?
Some objects reflect radar waves so efficiently that they appear extremely bright in images. These are called corner reflectors, and they typically occur when two surfaces meet at right angles, like the corner of a building or a bridge.
- In cities, streets and buildings create many right angles, causing strong radar reflections and appearing very bright in images.
- In nature, steep cliffs and rock formations can also act as corner reflectors, making some mountain areas highly visible in radar images.
For example, urban areas often have clusters of bright spots in radar images because of the numerous buildings, streetlights, and bridges reflecting the radar waves directly back to the sensor.
Why is Understanding Radar Image Brightness Important?
By knowing how surface and environmental factors influence brightness, we can:
- Improve flood prediction and waterlogging detection.
- Monitor agriculture and soil moisture.
- Plan urban development and infrastructure.
- Track climate change and environmental degradation.
In short, Radar Image Brightness is not just about image appearance—it’s a powerful tool for real-world applications.





























