Remote sensing is an important technology used in various fields, from environmental monitoring to urban planning. It involves collecting information about objects or areas from a distance, usually using satellites or aircraft. Remote sensing systems are broadly categorized into passive vs active Remote sensing. Both types have unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. Let’s explore them in detail.
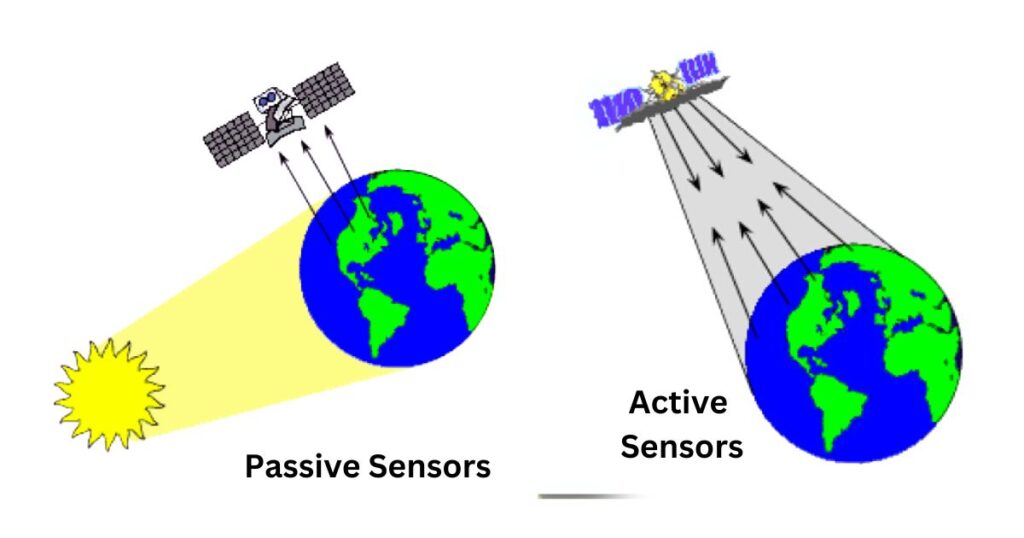
What is Passive Sensing?
Passive sensing relies on naturally available energy sources, primarily the sun. These sensors detect energy that is either:
- Reflected sunlight, like in visible and near-infrared wavelengths.
- Emitted energy, such as thermal infrared radiation from the Earth.
Key Characteristics of Passive Sensors:
- Works only when natural energy is available (e.g., sunlight).
- Cannot function at night for reflected energy (but can detect emitted energy like thermal infrared).
- Commonly used in weather forecasting, land cover mapping, and environmental studies.
Examples of Passive Sensors:
Optical cameras, Infrared sensors and Radiometers
What is Active Sensing?
Unlike passive sensors, active sensors generate their own energy to illuminate the target. They emit radiation, which then reflects off the object and returns to the sensor for measurement.
Key Characteristics of Active Sensors:
- Works anytime, regardless of sunlight or weather conditions.
- Can capture data in wavelengths not provided by the sun, like microwaves.
- Requires a large amount of energy to function.
Examples of Active Sensors:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): Used for mapping terrain, detecting changes in forests, and monitoring disasters.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Used in topographic mapping, forestry, and autonomous vehicles.
Passive vs Active Remote Sensing: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Passive Remote Sensing | Active Remote Sensing |
| Energy Source | Sunlight or naturally emitted energy | Own energy source |
| Functioning Time | Works in daylight (for reflected energy) | Works day and night |
| Weather Dependency | Can be affected by clouds | Works in all weather conditions |
| Energy Requirement | Does not require external energy | Requires high energy input |
| Examples | Optical cameras, radiometers | SAR, LiDAR |
Which One is Better?
Both passive and active sensing have their own advantages, and the choice depends on the application.
- If natural light is available and energy efficiency is important, passive sensors are preferred.
- If 24/7 monitoring is required or specific wavelengths need to be captured, active sensors are the better option.
Conclusion
Remote sensing plays a vital role in various industries, from agriculture to defense. Understanding the difference between passive and active sensing helps in selecting the right technology for specific needs. While passive sensing relies on natural energy sources, active sensing provides flexibility and control, making both indispensable in modern-day applications.





























